อ้างอิง:
ข้อความเดิมเขียนโดยคุณ HIGG BOZON
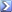
คุณสมบัติ metric คือ
1. $d(x,y)\geqslant 0$
2. $d(x,y)=0 \leftrightarrow x=y$
3. $d(x,y)=d(y,x)$
4. $d(x,y)\leqslant d(x,z)+d(z,y)$
คุณสมบัติ norm คือ
1. $\left\Vert\,x\right\Vert = 0 \leftrightarrow x=\theta $
2. $\left\Vert\,x+y\right\Vert \leqslant \left\Vert\,x\right\Vert +\left\Vert\,y\right\Vert $
3. $\left\Vert\,\alpha x\right\Vert = \left|\,\alpha \right|\left\Vert\,x\right\Vert $
อย่างนี้ถ้าผมจะเอานิยาม norm มาสร้าง metric ก็สร้างเงื่อนไขเพิ่มว่า $d(kx,ky)=k\cdot d(x,y)$ ถูกมั้ยครับ???? แล้วตรงอสมการสามเหลี่ยมนี่ต้องนิยามอะไรเพิ่มมั้ยครับ????? แล้วอย่างไหนเรียก necessary condition อย่างไหนเรียก sufficient condition อ่าครับ????   |
$d(kx,ky)=|k|\cdot d(x,y)$
อันนี้คือ necessary condition คิดว่าน่าจะมีอีกเงื่อนไขนึงคือ
$d(x,y)=d(x-y,0)$ ครับ จึงจะได้เงื่อนไขที่เพียงพอ
Proposition Let $X$ be a vector space and $d$ be a metric on $X$. Then $d$ induces a norm on $X$ if and only if
(a) $d(kx,ky)=|k|d(x,y)$ for all $k\in\mathbb{F}$ and $x,y\in X$
(b) $d(x,y)=d(x-y,0)$ for all $x,y\in X$
Proof: $(\Rightarrow)$ Obvious.
$(\Leftarrow)$ Suppose the converse holds. Define $\|x\|=d(x,0)$. Then $d(x,y)=d(x-y,0)=\|x-y\|$. We will show that $\|\cdot\|$ is a norm on $X$. Let $x,y\in X$ and $k\in\mathbb{F}$.
(1) $\|x\|=d(x,0)\geq 0$ and $\|x\|=0$ if and only if $x=0$.
(2) $\|kx\|=d(kx,0)=|k|d(x,0)=|k|\|x\|$
(3) $\|x+y\|=d(x+y,0)=d(x,-y)\leq d(x,0)+d(0,-y)=d(x,0)+d(0,y)=\|x\|+\|y\|$