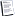
In mathematics, a line integral is an integral where the function to be integrated is evaluated along a curve.[1]
The terms path integral, curve integral, and curvilinear integral are also used;
contour integral is used as well, although that is typically reserved for line integrals in the complex plane.
The function to be integrated may be a scalar field or a vector field.
The value of the line integral is the sum of values of the field at all points on the curve,
weighted by some scalar function on the curve
(commonly arc length or, for a vector field,
the scalar product of the vector field with a differential vector in the curve).
This weighting distinguishes the line integral from simpler integrals defined on intervals.
In mathematics, particularly multivariable calculus,
a surface integral is a generalization of multiple integrals to integration over surfaces.
It can be thought of as the double integral analogue of the line integral.
Given a surface, one may integrate a scalar field
(that is, a function of position which returns a scalar as a value)
over the surface, or a vector field
(that is, a function which returns a vector as value).
If a region R is not flat, then it is called a surface as shown in the illustration.

|